GeoServer Blog
GeoServer 2.25-RC Release
GeoServer 2.25-RC release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is a release candidate intended for public review and feedback. GeoServer 2.25-RC is made in conjunction with GeoTools 31-RC, and GeoWebCache 1.25-RC.
Thanks to Jody Garnett (GeoCat) for making this release.
Why share a release candidate?
A sensible question to ask is why a “release candidate” is being produced at all - when we do not recommend running such a thing in production.
GeoServer also follows a “release early, release often” approach which is where the project shares releases so you can test and provide feedback.
This results in a lovely balance:
-
The GeoServer developer has already tested on the data and data sources they got handy.
-
The users of GeoServer have access to a much greater variety in data and and use cases to test with.
Please try out this release candidate and let us know how it works for you.
-
Bonus: By testing with your data directory you are assured that the next GeoServer will work well for you and your team.
This balance of a community sharing and each doing what they can they can do easily, is a nice thing about the open-source approach: the result is software we can trust and works well.
Thank you for being part of the GeoServer community. Testing and feedback is welcome by email and bug reports.
Upgrade Notes
We have a number of configuration changes when updating an existing system:
-
The longstanding
ENTITY_RESOLUTION_ALLOWLISTsetting has been recommended as a way to control the locations available for external entity resolution when parsing XML documents and requests.The default has changed from
*(allowing any location) to allowing the recommendedwww.w3.org,schemas.opengis.net,www.opengis.netlocations used for OGC Web Services, along with theinspire.ec.europa.eu/schemaslocation used by our friends in Europe. -
The FreeMarker Template HTML Auto-escaping is now enabled by default.
-
The spring security firewall is now enabled by default.
-
A new configuration setting is available to limit content served from the
geoserver/wwwfolder.If you have not met the
wwwfolder before it is used to share content, and there is a tutorial serving static files. -
We do add recommendations to production considerations over time, if you have not checked that page in a while please review.
Thanks to Steve Ikeoka and Jody Garnett for these improvements.
Security Considerations
This a reminder to update to GeoServer 2.24.2 Release (or GeoServer 2.35.5 Release).
Alongside the upcoming GeoServer 2.25.0 release we will “publicly disclose” a list of Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures that have been addressed previously.
- If you are working with a commercial support provider that volunteers with the geoserver-security email list they are already informed.
- If you have updated to GeoServer 2.24.2 Release (or GeoServer 2.23.5 Release) you are already patched.
I hope you enjoy our team’s effort to improve communication. The use of the CVE system allows us to reach a wider audience than reads these blog posts.
See the project security policy for more information on how security vulnerabilities are managed.
Experimental Java 21 support
GeoServer, along with GeoTools and GeoWebCache, are now tested to build and pass tests with Java 21.
This is not yet an endorsement to run GeoServer in production with Java 21. We are looking ahead at the 2024 roadmap, and are making sure the basics are covered for the newer Java releases.
JTS fast polygon intersection enabled by default
The JTS Next Generation polygon intersection algorithm has been enabled by default, which will improve performance of a number of operations, including WPS processes and the vector tiles generation.
We deem the functionality well tested enough that it should be opened to the majority of users, even if it’s still possible to turn it off by adding the -Djts.overlay=old.
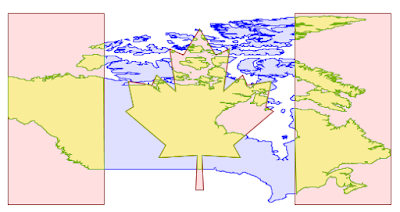
MapML Extension
The MapML extension is receiving a number of updates and improvements, with more to come in the following months. It’s now possible to declare “Tiled CRS” as the CRS for a layer, with the implication not just of the CRS, but also of the gridset that will be used by the MapML viewer:
This portion builds on top of the work done months ago to support astronomical CRSs, which allows GeoServer to support multiple CRS authorities.
The MapML preview links are now using the new MapML output format, while the old dedicated REST controller has been removed. This allows for better integration of the MapML format in the GeoServer ecosystem. The MapML viewer has also been updated to the latest version:
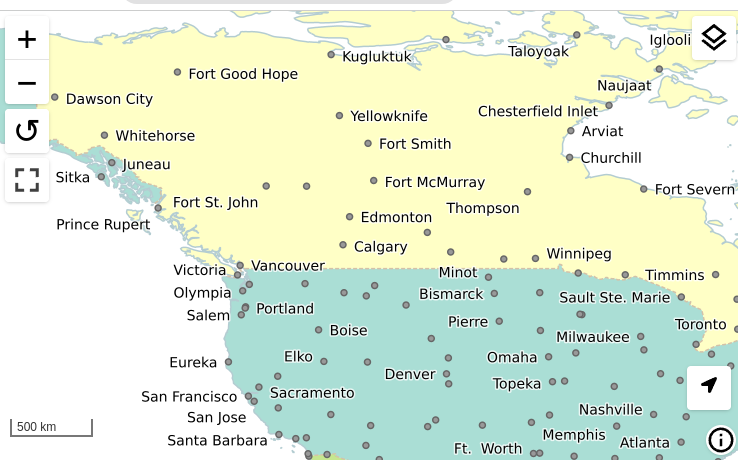
Thanks to Joseph Miller and Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions) for this work, and Natural Resources Canada for sponsoring it.
Community Module Updates
Much of the new activity in GeoServer starts as a community module. We’d like to remind you that these modules are not yet supported, and invite you to join the effort by participating in their development, as well as testing them and providing feedback.
Raster attribute Table community module
Developed as part of GEOS-11175, the Raster Attribute Table community module uses the GDAL Raster Attribute Table (RAT) to provide a way to associate attribute information for individual pixel values within the raster, to create styles as well as to provide a richer GetFeatureInfo output.


For more information see the user guide.
We’d like to thank Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions) for the development and NOAA for sponsoring.
Graticules for WMS maps
The graticules community module, developed as part of GEOS-11216, provides a datastore generating graticules for WMS maps, along with a rendering transformation that can be used to label them. The module can be used to draw a graticule in WMS maps, as well as to download them as part of WFS (or in combination with the WPS download module).


We’d like to thank Ian Turton for development and GeoSolutions for sponsoring the work.
GeoServer monitor Kafka storage
The monitoring Kafka storage module, developed as part of GEOS-11150, allows storing the requests captured by the monitoring extension into a Kafka topic.

We’d like to thank Simon Hofer for sharing his work with the community. To learn more about the module, how to install and use it, see the user-guide.
JWT Headers
The JWT headers module has been developed as part of GEOS-11317.

The module is a new authentication filter that can read JWT Headers, as well as general JSON payloads and simple strings, to identify a user, as well as to extract their roles. The combination of Apache mod_auth_openidc with geoserver-jwt-headers-plugin provides an alternative to using the geoserver-sec-oauth2-openid-connect-plugin plugin.
We’d like to thank David Blasby (GeoCat) for this work on this module.
Full Release notes
New Feature:
- GEOS-11225 [AuthKey] AuthKey synchronize the user/group automatically
MapML:
- GEOS-10438 ENTITY_RESOLUTION_ALLOWLIST property not parsing empty setting
- GEOS-11207 Refactor MapML MVC controller as GetMap-based operation with standard parameter format
- GEOS-11221 mkdocs preflight rst fixes
- GEOS-11289 Enable Spring Security StrictHttpFirewall by default
- GEOS-11297 Escape WMS GetFeatureInfo HTML output by default
- GEOS-11300 Centralize access to static web files
Improvement:
- GEOS-11306 Java 17 does not support GetFeature lazy JDBC count(*)
- GEOS-11130 Sort parent role dropdown in Add a new role
- GEOS-11142 Add mime type mapping for yaml files
- GEOS-11148 Update response headers for the Resources REST API
- GEOS-11149 Update response headers for the Style Publisher
- GEOS-11152 Improve handling special characters in the Simple SVG Renderer
- GEOS-11153 Improve handling special characters in the WMS OpenLayers Format
- GEOS-11155 Add the X-Content-Type-Options header
- GEOS-11173 Default to using HttpOnly session cookies
- GEOS-11176 Add validation to file wrapper resource paths
- GEOS-11213 Improve REST external upload method unzipping
- GEOS-11222 Include Conformance Class for “Search” from OGC API - Features Part 5 proposal
- GEOS-11226 Enable JTS OverlayNG by default
- GEOS-11246 Schemaless plugin performance for WFS
- GEOS-11247 Avoid HTML annotations special status in APIBodyProcessor
- GEOS-11248 Move version header handling from APIBodyMethodProcessor to APIDispatcher
- GEOS-11260 JNDI tutorial uses outdated syntax
- GEOS-11288 Improve input validation in ClasspathPublisher
- GEOS-11289 Enable Spring Security StrictHttpFirewall by default
- GEOS-11298 When a Raster Attribute Table is available, expose its attributes in GetFeatureInfo
Bug:
- GEOS-11050 jdbc-store broken by changes to Paths.names
- GEOS-11051 Env parametrization does not save correctly in AuthKey extension
- GEOS-11145 The GUI “wait spinner” is not visible any longer
- GEOS-11182 Avoid legends with duplicated entries
- GEOS-11187 Configuring a raster with NaN as NODATA results in two NaN in the nodata band description
- GEOS-11190 GeoFence: align log4j2 deps
- GEOS-11203 WMS GetFeatureInfo bad WKT exception for label-geometry
- GEOS-11224 Platform independent binary doesn’t start properly with default data directory
- GEOS-11250 WFS GeoJSON encoder fails with an exception if an infinity number is used in the geometry
- GEOS-11278 metadata: only selected tab is submitted
- GEOS-11312 Used memory calculation fix on legend WMS request
Task:
- GEOS-11242 Remove the Xalan library
- GEOS-11315 Revert to CORS commented out
- GEOS-11318 Update postgresql to 42.7.2
- GEOS-11134 Feedback on download bundles: README, RUNNING, GPL html files
- GEOS-11141 production consideration for logging configuration hardening
- GEOS-11159 Update mapfish-print-lib 2.3.0
- GEOS-11180 Update ImageIO-EXT to 1.4.9
- GEOS-11181 Update jai-ext to 1.1.25
- GEOS-11186 Fix maven enforcer failFast
- GEOS-11220 Upgrade Hazelcast from 5.3.1 to 5.3.6
- GEOS-11245 Update OSHI from 6.2.2 to 6.4.10
- GEOS-11316 Update Spring version to 5.3.32
Community module development:
- GEOS-11305 Add layer information in the models backing STAC
- GEOS-11146 Fix MBTiles output format test
- GEOS-11184 ncwms module has a compile dependency on gs-web-core test jar
- GEOS-11209 Open ID Connect Proof Key of Code Exchange (PKCE)
- GEOS-11212 OIDC accessToken verification using only JWKs URI
- GEOS-11219 Upgraded mail and activation libraries for SMTP compatibility
- GEOS-11293 Improve performance of wps-lontigudinal-profile
About GeoServer 2.25 Series
Additional information on GeoServer 2.25 series:
Release notes: ( 2.25-RC )
GeoServer 2.23.5 Release
GeoServer 2.23.5 release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is the last planned maintenance release of GeoServer 2.23.x, providing existing installations with minor updates and bug fixes. Sites using the 2.23.x series are encouraged to upgrade to GeoServer 2.24.x, or eventually wait next month, for the 2.25.0 release, and upgrade their installation, with the help of the upgrade guide.
GeoServer 2.23.5 is made in conjunction with GeoTools 29.5, and GeoWebCache 1.23.4.
Thanks to Andrea Aime (GeoSolutions) for making this release.
Security Considerations
This release addresses security vulnerabilities and is considered an essential upgrade for production systems.
- CVE-2024-23634 Arbitrary file renaming vulnerability in REST Coverage/Data Store API (Moderate).
See project security policy for more information on how security vulnerabilities are managed.
Release notes
New Feature:
- GEOS-11225 AuthKey synchronize the user/group automatically
- GEOS-11279 metadata: allow same field on multiple tabs
Improvement:
- GEOS-11213 Improve REST external upload method unzipping
- GEOS-11246 Schemaless plugin performance for WFS
- GEOS-11260 JNDI tutorial uses outdated syntax
- GEOS-11276 Use style_body to define CSS style for a layer
- GEOS-11288 Improve input validation in ClasspathPublisher
Bug:
- GEOS-11174 GWC rest api returns erroneous truncated response when gzip http encoding is enabled
- GEOS-11205 Layer page: style image fails if it is in isolated workspace
- GEOS-11250 WFS GeoJSON encoder fails with an exception if an infinity number is used in the geometry
- GEOS-11255 Multiple inserts in WPS with different idGen strategies does not work
- GEOS-11256 Cannot retrieve LegendGraphic from a PostGIS datastore with ‘hideEmptyRules’ and ‘Support on the fly geometry simplification’ enabled
- GEOS-11278 metadata: only selected tab is submitted
- GEOS-11285 GWC REST Content-Encoding gzip returns broken response
- GEOS-11291 GeoFence: Cleanup stale log4j references
For the complete list see 2.23.5 release notes.
Community Updates
Community module development:
- GEOS-10933 keycloak logout NPE
- GEOS-11290 With Oauth enabled, anon users get random auth requests
Community modules are shared as source code to encourage collaboration. If a topic being explored is of interest to you, please contact the module developer to offer assistance.
About GeoServer 2.23 Series
Additional information on GeoServer 2.23 series:
- GeoServer 2.23 User Manual
- Drop Java 8
- GUI CSS Cleanup
- Add the possibility to use fixed values in Capabilities for Dimension metadata
- State of GeoServer 2.23
- GeoServer Feature Frenzy 2023
- GeoServer used in fun and interesting ways
- GeoServer Orientation
Release notes: ( 2.23.5 | 2.23.4 | 2.23.3 | 2.23.2 | 2.23.1 | 2.23.0 | 2.23-RC1 )
A Comprehensive Guide to Publishing a Shapefile in GeoServer
GeoSpatial Techno is a startup focused on geospatial information that is providing e-learning courses to enhance the knowledge of geospatial information users, students, and other startups. The main approach of this startup is providing quality, valid specialized training in the field of geospatial information.
( YouTube | LinkedIn | Facebook | Reddit | X )
A Comprehensive Guide to publishing a Shapefile in GeoServer
In this session, we want to talk about “How to Publish Shapefile in GeoServer” comprehensively. If you want to access the complete tutorial, simply click on the link
Introduction
The Data section contains configuration options for all the different data-related settings that GeoServer uses to access and publish geospatial information. It also describes how to load, manage, and publish data in the GeoServer web interface. Each section contains the specific pages that provide add, view, edit, and delete capabilities.
Note. In this blog post, we used GeoServer version 2.20.0.
Workspaces
A Workspace serves as a means to group and organize similar layers together. It enables you to associate multiple layers and stores with a single workspace. Each workspace can be managed independently, with its own security policies, data administrator, and web services. Generally, a workspace is created for each project, along with its corresponding stores and layers.
Add a workspace
To create a new workspace, navigate to Data > Workspaces page. Click on the Add new workspace, then you have to enter a Workspace Name and Namespace URI.
- Workspace Name: It is an identifier describing your project. It must not exceed ten characters or contain spaces (due to use as an XML “prefix” when downloading content).
- Namespace URI: URI stands for Uniform Resource Identifier, is a formal system for uniquely identifying resources, and consists of two types: URL and URN. A Namespace URI does not need to point to an actual location on the web and only needs to be a unique identifier.
- Default Workspace: This setting is useful when you only have one workspace defined. The setting allows users to communicate with the web service using just the layer name (rather than prefix:layer name required when managing hundreds of workspaces). select the Default Workspace checkbox to assign this as your default workspace.
- Sometimes the same feature type needs to be published multiple times with a different mapping and with the same name. This can be done in GeoServer using Isolated Workspaces functionality.
Press the Submit button to save your new workspace.
Edit a workspace
To view or edit a workspace, click on the Workspace name, then a workspace configuration page will be displayed.
- For Settings, select the Enabled checkbox to customize the settings and contact details for the workspace level. This allows you to define an introduction to your workspace, and override the global settings for your workspace.
- Use the checkbox located next to each service to override the Global Settings for the associated service. Once enabled, clicking on the Services link will open the settings page for the service, allowing default values for the service title, abstract, and other details to be supplied.
- The Security tab allows to set data access rules at the workspace level. To create/edit the workspace’s data access rules, check/uncheck checkboxes according to the desired role.
Remove a workspace
To remove a workspace, select it by clicking the checkbox next to the workspace. Multiple workspaces can be selected, or all can be selected by clicking the checkbox in the header. Click the Remove selected workspace(s) link. Now you will be asked to confirm or cancel the removal.
Pressing OK removes the selected workspace(s).
Stores
The Stores manage the connection parameters between GeoServer and the data sources where your spatial data reside. They provide a mechanism for GeoServer to connect to various data repositories, including file systems, databases, and cloud storage services. Each store represents a unique data source and has its configuration settings.
Add a store
To add a Store, navigate to Data > Stores page. Click on Add new store, then you will be prompted to choose a data source. GeoServer supports several different data formats, but they are classified into three types: “Vector data”, “Raster data”, and “Cascaded Services”.
- Vector data formats include Shapefile, GeoPackage, PostGIS, and Properties. The most common and widely used option is Shapefile.
- Raster data formats include ArcGrid, GeoPackage, GeoTIFF, ImageMosaic, and WorldImage. The most used and well-known are the GeoTIFF and the WorldImage. GeoTIFF is a spatial extension of the “TIFF” format and tags image files with geographic information. A WorldImage is similar, but georeferencing information is saved in an external text file.
- Cascaded Services include WFS, WMS, and WMTS. GeoServer can proxy a remote Web Map Service and Web Map Tile Service and load it as a store in GeoServer.
Other data sources are supplied as GeoServer extensions. Extensions are downloadable modules that add functionality to GeoServer. Click the appropriate data source to configure the store, because the connection parameters vary depending on data format.
To create a Shapefile data store, follow these steps:
- Select the desired workspace from the drop-down menu.
- Enter the
Data Source Name. Make sure the “Enabled” checkbox is selected. Otherwise, access to the store along with all the datasets defined, will be disabled for it. - In the “Shapefile location”, click on the Browse link to define the location of the shapefile.
- The DBF file format has a field for character encoding, but it doesn’t always accurately indicate the actual encoding used. As a result, it is important to specify the DBF character set correctly when decoding strings to ensure accurate interpretation of the data.
When finished, press the Save button. Now it will automatically redirect to the Add New Layer page, which will be completely described in the Layer section. Next, we will explain how to edit and remove the store.
Edit a store
To view or edit a store, click on the Store name. A Store configuration page will be displayed. The exact contents of this page depend on the specific format of the Store. After your configuration is modified, press the Save button.
Remove a store
To remove a Store, click the checkbox next to the store. Multiple stores can be selected, or all can be selected by clicking the checkbox in the header. Click the Remove selected stores. You will be asked to confirm the removal of the configuration for the store(s) and all resources defined under them.
Pressing OK removes the selected Store(s), and returns to the Stores page.
Layers
From the administration interface, navigate to the Data > Layers page. On this page, you can view and edit existing layers, add a new layer, or remove a layer. It also shows you the type of layers in the Type column, with a different icon for vector and raster layers, according to the geometry shape. The Title, Workspace, and Store values of each layer are shown.
Add a layer
Clicking the Add a new layer, brings up a New Layer Chooser panel. The menu displays all currently enabled stores. If you want to add a new layer for a published resource, click on Publish Again. Note that when republishing the name of the new layer may have to be modified to avoid conflict with an existing layer.
The beginning sections (Basic Resource Info, Keywords, and Metadata link) provide metadata, specifically textual information that makes the layer data easier to understand and work with. The metadata information will appear in the capabilities documents which refer to the layer. These options are:
- Name: The identifier used to reference the layer in WMS requests that are filled automatically. Note that for a new layer for an already-published resource, the name must be changed to avoid conflict.
- Enabled: A layer that is not enabled won’t be available to any kind of request, it will just show up in the configuration and in REST config.
- Advertised: A layer is advertised by default. A non-advertised layer will be available in all data access requests (for example, WMS GetMap, WMS GetFeature) but won’t appear in any capabilities document or the layer preview.
- Title: The human-readable description to briefly identify the layer to clients that filled automatically. GeoServer provides an item for the title and abstract and describes how to specify metadata in different languages. By default, it’s disabled and can be enabled from the i18n checkbox.
- Abstract: It describes the layer in detail.
- Keywords: List of short words associated with the layer to assist catalog searching. To add a new keyword, enter your keyword, then press the Add Keyword button to add it.
- Metadata & Data Links: It allows linking to external documents that describe the data layer. The
Typeinput provides a few example types, like FGDC or ISO19115, but allows any other type to be declared.Formatprovides its mime type, whileURLpoints to the actual metadata.
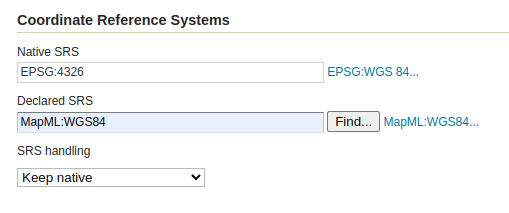
A Coordinate Reference System (CRS) defines how georeferenced spatial data relates to real locations on the Earth’s surface. GeoServer needs to know the CRS of your data. This information is used for computing the latitude/longitude bounding box and reprojecting the data during both WMS and WFS requests.
- Native SRS: Specifies the coordinate system the layer is stored in. Clicking the projection link displays a description of the SRS.
- Declared SRS: Specifies the coordinate system GeoServer publishes to clients.
- SRS Handling: Determines how GeoServer should handle projection when the two SRSes differ. Possible values are:
- Force declared: This is the default option and normally the best course of action. Use this option when the source has no native CRS, has a wrong one, or has one matching the EPSG code.
- Reproject from native: This setting should be used when the native data set has a CRS that does not match any official EPSG. E.g.
Lambert Conformal Conic to WGS84. - Keep native: This is a setting that should be used in very rare cases. Keeping native means using the declared one in the capabilities documents, but then using the native CRS in all other requests.
The Bounding Box determines the extent of the data within a layer. It includes two items: “Native Bounding Box” and “Lat/Lon Bounding Box”. Generate the bounds for the layer by pressing the Compute from data and Compute from native bounds button in the Bounding Boxes section.
Vector layers have a list of the “Feature Type Details”. These include the Property and Type of a data source. Remember that, if you want to change your data by ArcGIS or QGIS, like add or remove features or fields, or edit the attribute table contents, there is no need to create a layer again in the GeoServer, just press the Reload feature type, so your layer will be updated.
Remember that GeoServer, by default, publishes all the features that are currently available in the layer. However, if you wish to limit the features to a specific subset, you can achieve this by specifying a CQL filter in the configuration. Upon completing the layer configuration, finalize the process by pressing the Save button. This action will create the layer based on the specifications you have provided.
Edit a layer
To view or edit a layer, click on the Layer Name from the Layer page. A layer configuration page will be displayed. After your configuration is modified, press the Save button.
Remove a layer
To remove a layer, select the checkbox next to the layer. Multiple layers can be selected, or all can be selected by clicking the checkbox in the header. By clicking the Remove selected layers link, you will be asked to confirm the removal of the configuration for the layer(s) and all resources defined under them.
Press OK removes the selected layer(s), and returns to the Layers page.
GeoServer 2.24.2 Release
GeoServer 2.24.2 release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is a stable release of GeoServer recommended for production use. GeoServer 2.24.2 is made in conjunction with GeoTools 30.2, and GeoWebCache 1.24.2.
Thanks to Jody Garnett (GeoCat) for making this release, everyone who contributed, and to Georg Weickelt and Peter Smythe for preflight testing.
Security Considerations
This release addresses security vulnerabilities and is considered an essential upgrade for production systems.
- CVE-2024-23634 Arbitrary file renaming vulnerability in REST Coverage/Data Store API (Moderate).
See project security policy for more information on how security vulnerabilities are managed.
Release notes
Improvement:
- GEOS-11213 Improve REST external upload method unzipping
- GEOS-11246 Schemaless plugin performance for WFS
- GEOS-11219 Upgraded mail and activation libraries for SMTP compatibility
Bug:
- GEOS-9757 Return a service exception when client provided WMS dimensions are not a match
- GEOS-11051 Env parametrization does not save correctly in AuthKey extension
- GEOS-11223 Layer not visible in preview/capabilities if security closes the workspace, but allows access to the layer
- GEOS-11224 Platform independent binary doesn’t start properly with default data directory
- GEOS-11235 preauthentication filters - session reuse even after having logout
- GEOS-11241 ModificationProxy breaks information hidding on CatalogInfo.accept(CatalogVisitor) exposing the proxied object
- GEOS-11250 WFS GeoJSON encoder fails with an exception if an infinity number is used in the geometry
- GEOS-11255 Multiple inserts in WPS with different idGen strategies does not work
Task:
- GEOS-11220 Upgrade Hazelcast from 5.3.1 to 5.3.6
- GEOS-11245 Update OSHI from 6.2.2 to 6.4.10
For the complete list see 2.24.2 release notes.
Community Updates
Community module development:
- GEOS-10933 keycloak logout NPE
Community modules are shared as source code to encourage collaboration. If a topic being explored is of interest to you, please contact the module developer to offer assistance.
About GeoServer 2.24 Series
Additional information on GeoServer 2.24 series:
GeoServer About & Status - A Practical Guide
GeoSpatial Techno is a startup focused on geospatial information that is providing e-learning courses to enhance the knowledge of geospatial information users, students, and other startups. The main approach of this startup is providing quality, valid specialized training in the field of geospatial information.
( YouTube | LinkedIn | Facebook | Reddit | X )
GeoServer About & Status along with practical guides
In this session, we would like to talk around the “About & Status” section of GeoServer. If you want to access the complete tutorial, simply click on the link
Introduction
The “About & Status” section of GeoServer provides information about runtime variables and how GeoServer is described to clients that connect to it. In other words, this section provides access to GeoServer diagnostic and configuration tools and can be particularly useful for debugging.
- “Server Status”: view server configuration and run-time status.
- “GeoServer Logs”: see GeoServer log output for error diagnosis.
- “Contact Information”: manage public contact details for WMS server.
- “About GeoServer”: access GeoServer docs, homepage, and bug tracker. You do not need to be logged into GeoServer to access this page.
Server Status
The “Server Status” page, gives you a summarized overview of the main configuration parameters and information about the current state of the GeoServer. It has three tabs:
- The “Status” tab, provides a summary of server configuration parameters and run-time status.
- The “Modules” tab, provides the status of the various modules installed on the server.
- The “System Status” tab, provides extra information about the system environment GeoServer is running in.
Status Field Descriptions
This page describes the current status indicators:
- Data directory: It shows the path to the GeoServer data directory. The procedure for setting the location of the GeoServer data directory is dependent on the type of GeoServer installation. When running a GeoServer Web Archive inside a servlet container, the data directory can be specified in several ways. The recommended method is to set a servlet context parameter. To specify the data directory using a servlet context parameter, create the “context-param” element in the “WEB-INF/web.xml” file for the GeoServer application. After you change the path of the data directory, log in to GeoServer again. Now you can see the new path of the data directory.
- Locks: When using Transactional Web Feature Service (WFS-T), clients can edit feature types. To prevent data corruption, GeoServer locks the data during transactions. If the number is greater than one, there are active transactions. Clicking “Free Locks” resets a hung editing session and removes any abandoned locks.
- Connections: This shows you the number of vector data store connections. Vector data stores are repositories configured for the persistence of features.
- Memory Usage: This shows you how much memory GeoServer is using. You can manually run the garbage collector by clicking the Free Memory button, so it cleans up memory marked for deletion.
- JVM Version: This is the version of the “Java Virtual Machine” that the GeoServer is using.
- Java Rendering Engine: It shows the rendering engine used for vector operations.
- Available Fonts: This is a list of the fonts seen by the GeoServer. Fonts are useful to render labels for spatial features. Selecting the link will show the full list. To add custom fonts to the GeoServer, first, you have to download your favorite fonts from the web, then copy them to the “Java installation folder\jre\lib\fonts”. After restarting the Apache Tomcat software, the new fonts will be added to the Available Fonts list.
In programming, to improve the speed and performance of the program, each of the various tasks and parts of the application can be assigned to a thread. The Thread Pool template helps conserve resources in a multithread application and also places parallel computations in a specific predefined framework. When using the Thread Pool, we can perform concurrent tasks in parallel form. Here are the titles of GeoServer’s ThreadPoolExecutor parameters: ThreadPoolExecutor Core Pool Size , ThreadPoolExecutor Max Pool Size , ThreadPoolExecutor Keep Alive Time(ms)
- Update Sequence: This option shows you how many times the server configuration has been updated.
- Resource cache: GeoServer does not cache data, but it does cache connection to stores, feature type definitions, external graphics, font definitions, and CRS definitions as well. The “Clear” button forces those caches to empty and makes GeoServer reopen the stores and re-read image and font information, as well as the custom CRS definitions stored in: ${GEOSERVER_DATA_DIR}/user_projections/epsg.properties
- Configuration and catalog: This option is very useful to update the configuration without having to restart the service. If the configuration on the disk becomes outdated due to external changes, you can refresh it by loading the latest data from the disk.
Module Field Descriptions
In GeoServer, a module can fall into one of three classes:
- Core, those modules that are visible by default in the Modules tab that GeoServer requires to function and are distributed with the main GeoServer distribution.
- Extension, those modules that add functionality to GeoServer. They are installed as add-ons to the base GeoServer installation. After you download and install these extensions, they are added to the Geoserver modules list. For example WPS extension
- Community, those modules that are generally considered experimental and are often under development. For that reason, Unlike the official extensions, these modules are not released and stored on SourceForge when an official GeoServer release is produced.
Every module added to GeoServer has its origin as a community module. If the module becomes stable enough it will eventually become part of the main GeoServer distribution either as a core module or as an extension.
System Status Field Descriptions
System Status adds some extra information about the system in the GeoServer status page in a tab named System Status and makes that info queryable through the GeoServer REST interface. This info should allow an administrator to get a quick understanding of the status of the GeoServer instance. If the System status tab is not present, it means that the plugin was not installed correctly. The System status tab content will be refreshed automatically every second.
GeoServer Logs
The “GeoServer Logs” page, lets you read the messages, warnings, and errors contained in the log file. According to the current logging settings, you can find more information about the requests clients send to GeoServer and how it processes them. You can only read the last 1,000 lines by default from the console. You can also change this setting, but if you need to access the entire log content, we would strongly suggest accessing it with a text editor.
You can use the “Download the full log file” link placed just under the text console, or access the log file directly from this path: “geoserver_data_dir/logs/geoserver.log”
Contact Information
The “Contact Information” page, is used in the Capabilities document of the WMS server and is publicly accessible. GeoServer provides an item to describe this information and metadata in different languages. By default, it’s disabled and can be enabled from the i18n checkbox. You can complete this form with the relevant information and press the Save button to save your information.
About GeoServer
The “About GeoServer” section, provides a brief description of geoserver and build information such as GeoServer Version, Git Revision, Build Date, GeoTools Version, and GeoWebCache Version. Also, this section provides links to the GeoServer Documentation, Wiki, and Issue Tracker. Remember that, You do not need to be logged into GeoServer to access this page.
Tutorials
- How to create Tile Layers with GeoServer
- How to style layers using GeoServer and QGIS
- How to Publish a GeoTIFF file in GeoServer
- A Comprehensive Guide to Publishing a Shapefile in GeoServer
- GeoServer About & Status - A Practical Guide
- GeoServer installation methods on Windows
- Introducing GeoSpatial Techno with a Video Tutorial
- GeoServer Presentations on FOSS4G 2019

